How do domains work?
- Md Sohel Rana
- Feb 4, 2024
- 1 min read
--------------
The internet is a vast global network of computers linked to one another by an extensive submerged cable system. All computers, be they personal devices or servers, are equipped with an IP address that enables them to connect to the rest of the network and exchange, locate, and access web content.
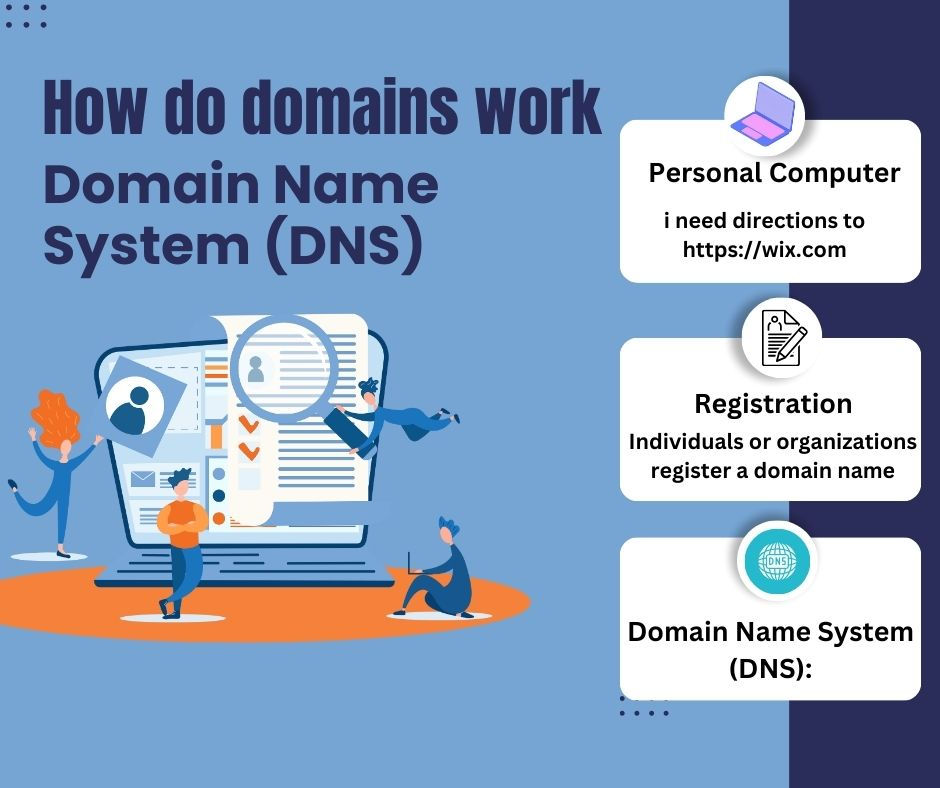
Simply said, domain names are these IP addresses' more approachable forms that are linked to certain websites. The seemingly random word strings must, however, return to numbers in order for computers to locate the correct web pages. The domain name system (DNS) is useful in this situation because Every domain name is converted into a computer-readable IP address via the DNS.
DNS servers receive a request from web browsers when they enter a domain name. DNS servers find the servers associated with that particular domain name and route your query to them. The web host is in charge of these so-called "name servers." They will submit the request to the web server that houses the specific website files after locating the pertinent IP. The web server locates all related files using the IP address and returns all information to the browser. These actions are completed in less than three seconds. Another name for a DNS or web server is a domain server.


Comments